Decision Making in C (if , if..else, Nested if, if-else-if )
There come situations in real life when we need to make some decisions and based on these decisions, we decide what should we do next. Similar situations arise in programming also where we need to make some decisions and based on these decisions we will execute the next block of code. For example, in C if x occurs then execute y else execute z. There can also be multiple conditions like in C if x occurs then execute p, else if condition y occurs execute q, else execute r. This condition of C else-if is one of the many ways of importing multiple conditions.
if statement is the most simple decision-making statement. It is used to decide whether a certain statement or block of statements will be executed or not i.e if a certain condition is true then a block of statements is executed otherwise not.
Syntax:
if(condition) { // Statements to execute if // condition is true }
Here, condition after evaluation will be either true or false. C if statement accepts boolean values – if the value is true then it will execute the block of statements below it otherwise not. If we do not provide the curly braces ‘{‘ and ‘}’ after if(condition) then by default if statement will consider the first immediately below statement to be inside its block.
Example:
if(condition) statement1; statement2; // Here if the condition is true, if block // will consider only statement1 to be inside // its block.
Flowchart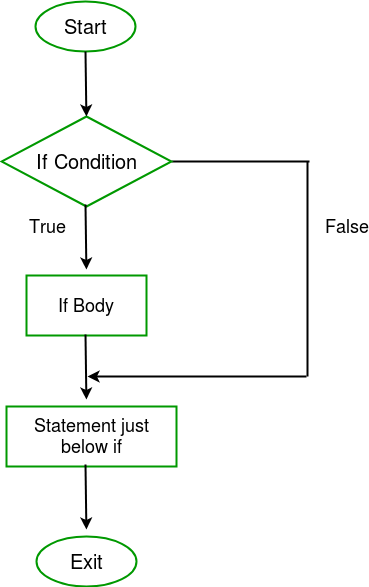
The if statement alone tells us that if a condition is true it will execute a block of statements and if the condition is false it won’t. But what if we want to do something else if the condition is false. Here comes the C else statement. We can use the else statement with if statement to execute a block of code when the condition is false.
Syntax:
if (condition)
{
// Executes this block if
// condition is true
}
else
{
// Executes this block if
// condition is false
}
Flowchart:
A nested if in C is an if statement that is the target of another if statement. Nested if statements means an if statement inside another if statement. Yes, both C and C++ allows us to nested if statements within if statements, i.e, we can place an if statement inside another if statement.
Syntax:
if (condition1) { // Executes when condition1 is true if (condition2) { // Executes when condition2 is true } }
Flowchart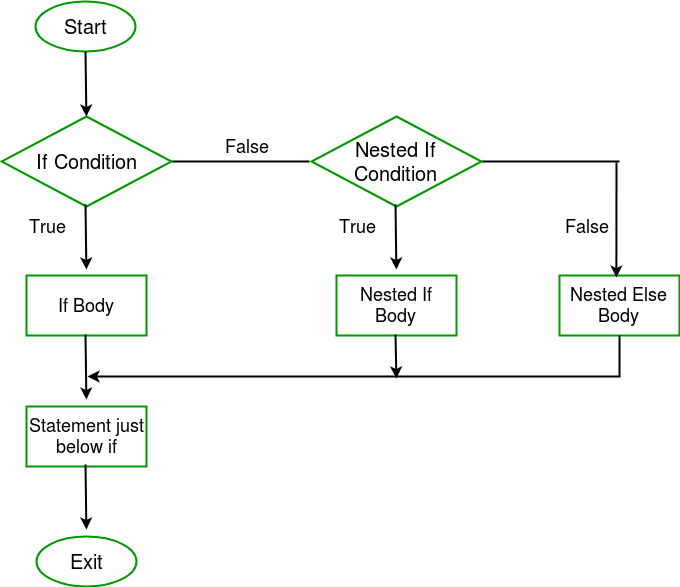
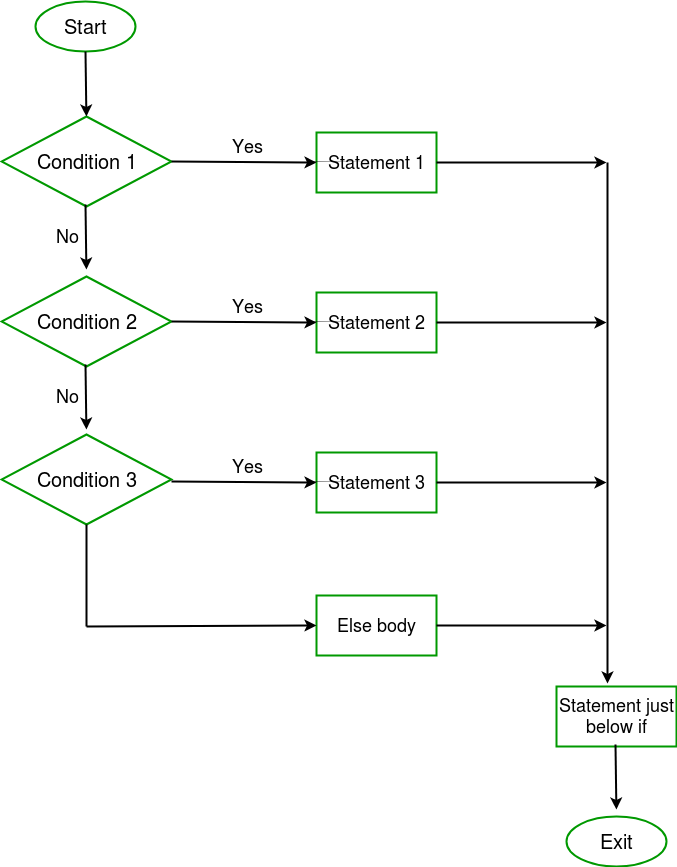
Here, a user can decide among multiple options. The C if statements are executed from the top down. As soon as one of the conditions controlling the if is true, the statement associated with that if is executed, and the rest of the C else-if ladder is bypassed. If none of the conditions are true, then the final else statement will be executed.
Syntax:
if (condition) statement; else if (condition) statement; . . else statement;